PROPELLER PUMPS
There are two basic types of propeller pumps, axial-flow and mixed-flow impellers. The axial-flow propeller pump is one having a flow parallel to the axis of the impeller. The mixed-flow propeller pump is one having a flow that is both axial and radial to the impeller.
VERTICAL WET WELL PUMPS
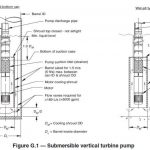
A vertical wet well pump is a vertical shaft, diffuser type centrifugal pump with the pumping element suspended from the discharge piping. The needs of a given installation determine the length of discharge column. The pumping bowl assembly may connect directly to the discharge head for shallow sumps, or may be suspended several hundred feet for raising water from wells. Vertical turbine centrifugal pump consists of multiple impellers that are staged on a vertical shaft. The impellers are designed to bring water in the bottom and discharge it out the top. This results in axial flow as water is discharged up through the column pipe. Staging the impellers in these pumps can create very high discharge pressures, since the pressure increases as the water moves through each stage.
POSITIVE DISPLACEMENT PUMPS
RECIPROCATING OR PISTON PUMPS
The word “reciprocating” means moving back and forth, so a reciprocating pump is one that moves water or sludge by a piston that moves back and forth. A simple reciprocating pump is shown below. If the piston is pulled to the left, check valve A will be open and sludge will enter the pump and fill the casing. When the piston reaches the end of its travel to the left and is pushed back to the right, Check Valve A will close, Check Valve B will open, and wastewater will be forced out the exit line.
A reciprocating or piston pump is a positive-displacement pump. Never operate it against a closed discharge valve or the pump, valve, and/or pipe could be damaged by excessive pressures. Also, the suction valve should be open when the pump is started. Otherwise an excessive suction or vacuum could develop and cause problems.
INCLINE SCREW PUMPS
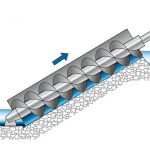
Incline screw pumps consist of a screw operating at a constant speed within a housing or trough. When the screw rotates, it moves the wastewater up the trough to a discharge point. Two bearings, one on top and one at the bottom, support the screw.