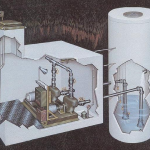
Dry Pit
A key advantage of dry-well lift stations is that they allow easy access for routine visual inspection and maintenance. In general, they are easier to repair than submersible pumps. An advantage of submersible lift stations is that they typically cost less than dry-well stations and operate without frequent pump maintenance. Submersible lift stations do not usually include large aboveground structures and tend to blend in with their surrounding environment in residential areas. They require less space and are easier and less expensive to construct.
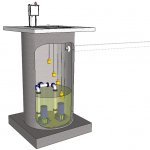
Pre-fabricated pump stations are available in various forms and can be either dry-well or submersible. Pre-fabricated pump stations are typically used for smaller flows because they are more compact and generally lower in cost than custom-designed pump stations. Pre-fabricated drywell pump stations usually include steel or plastic shell that is designed to house one to three vertical shaft flooded suction pumps. Pumps, valves and other equipment are installed at the factory prior to shipment.
Circular station shells are more common and larger pump stations can have an oval shape. Pump station shells are typically bolted to cast-in place concrete base slabs at the job site. In wet well configurations, the wet well usually is constructed of pre-cast concrete. Prefabricated submersible stations are typically constructed of pre-cast concrete or steel and can accommodate one or two submersible pumps. For pre-cast concrete stations, the pump manufacturer may provide a complete package of equipment, including submersible pumps, discharge elbows, check valves, access hatches, and level controls. For steel stations, the equipment is typically pre-packaged at the factory. Fiberglass tanks are typically used for smaller pump stations.
Calculating volumes:
What is the volume of a tank in cubic feet if it is 100 ft long, 30 ft wide and 20 ft deep?
The tank is a rectangle. Therefore the volume will equal length X width X height.
Volume = 100 ft X 30 ft X 20 ft = 60,000 ft3
What is the volume of asphalt removed in cubic feet if a manhole is to be constructed that is 25 feet in diameter and 6 inches deep?
This section removed from the asphalt would be a cylinder.
Length = (6 inches) / (12 in/ft) = 0.5 ft
diameter = 0.785 x D x D x Length OR radius = 3.14 X R X R X Length
(radius is 1/2 the diameter)
Volume = 0.785 x 25 ft x 25 ft x 0.5 ft = 245.31 ft3 OR 3.14 X 12.5 ft X 12.5 ft X 0.5 ft
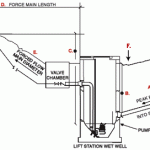
Lift stations are used to move wastewater from lower to higher elevation, particularly where the elevation of the source is not sufficient for gravity flow and/or when the use of gravity conveyance will result in excessive excavation depths and high sewer construction costs.
Lift stations are widely used in wastewater conveyance systems. Dry-well lift stations have been used in the industry for many years. However, the current industry-wide trend is to replace drywell lift stations of small and medium size (typically less than 24,000 liters per minute or 6,350 gallons per minute) with submersible lift stations mainly because of lower costs, a smaller footprint, and simplified operation and maintenance.
Variable speed pumping is often used to optimize pump performance and minimize power use. several types of variable-speed pumping equipment are available, including variable voltage and frequency drives, eddy current couplings, and mechanical variable speed drives. Variable-speed pumping can reduce the size and cost of the wet well and allows the pumps to operate at maximum efficiency under a variety of flow conditions. Because variable-speed pumping allows lift station discharge to match inflow, only nominal wet-well storage volume is required and the well water level is maintained at a near constant elevation.
Modern pump stations are equipped with automatic controls for pump starting and operational sequencing. The pump stations typically have standby pumps to increase reliability and provide adequate capacity for unusually high flows. In unattended pumping stations, automatic controllers are frequently used to allow switch over to standby units when a pump fails. Flow recording equipment is often installed to record instantaneous pumping rates and the total flow pumped.
The useful life of pump station equipment is typically limited to 20 to 30 years, with good maintenance. Pump station structures typically have a useful life of 50 years. The useful life of pump station equipment and structures can be prolonged by using corrosion-resistant materials and protective coatings.